Discover the Power of Air Source Heat Pumps
Join the growing trend towards energy efficiency and sustainability with air source heat pumps (ASHPs). As an alternative to traditional boilers, ASHPs offer a host of benefits that make them an attractive choice for modern homeowners and businesses alike.
Make the switch to air source heat pumps and unlock a world of benefits for your property and the planet. Contact us today to learn more about how ASHPs can revolutionize your heating and cooling experience while paving the way towards a sustainable future.
Efficiency Redefined
ASHPs boast superior efficiency compared to standard boilers, making them a smart investment for those seeking to reduce energy consumption and operating costs. By harnessing the renewable energy available in the air around us, these systems provide reliable heating and cooling while significantly lowering your carbon footprint.
Government Support
Take advantage of government incentives that can cover up to 75% of your installation costs, making the transition to ASHPs more affordable than ever. These financial incentives are designed to encourage the adoption of sustainable heating solutions, putting money back in your pocket while you contribute to a greener future.
Sustainable Solutions
Embrace a more sustainable lifestyle by choosing ASHPs as your primary heating and cooling solution. By utilizing ambient air as a heat source, ASHPs reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize environmental impact, making them a responsible choice for eco-conscious individuals and organizations.
Financial Savings
Experience long-term savings on energy bills with ASHPs, thanks to their high efficiency and reduced reliance on expensive fossil fuels. By optimizing energy usage and maximizing performance, these systems deliver year-round comfort without breaking the bank.
How Do Heat Source Air Pumps Work
Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) work by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it indoors to heat your home or building. They operate on the same principle as refrigerators but in reverse.
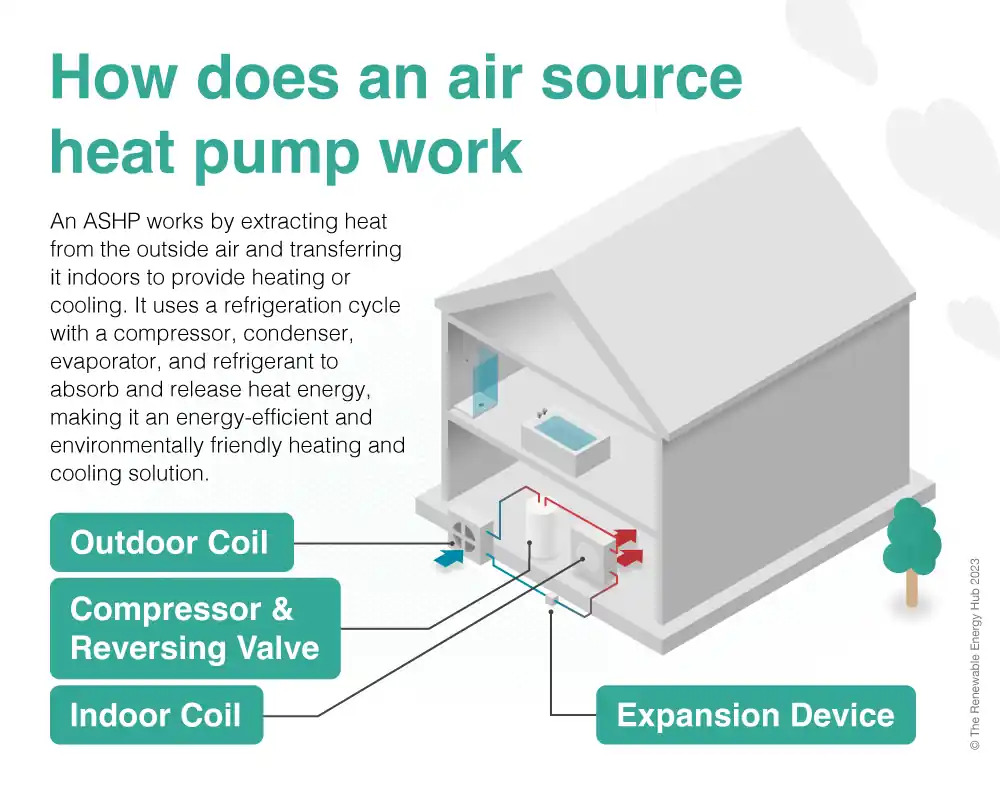
Absorption of Heat: The process begins with the outdoor unit of the ASHP absorbing heat from the surrounding air. Even in cold weather, there is still heat energy present in the air, which the heat pump’s outdoor unit captures using a refrigerant fluid.
Compression: The refrigerant fluid, now carrying the absorbed heat, is compressed by the ASHP’s compressor. Compression increases the temperature of the refrigerant, intensifying the heat energy it carries.
Heat Exchange: The compressed, high-temperature refrigerant fluid flows into the indoor unit of the ASHP, where it passes through a heat exchanger coil. In heating mode, this coil warms up the indoor air by transferring the heat from the refrigerant fluid to the indoor air. The heated air is then circulated throughout the building via ductwork or other distribution systems.
Expansion and Release: After transferring its heat to the indoor air, the refrigerant fluid undergoes expansion, which causes its temperature to drop. It then returns to the outdoor unit to repeat the cycle, absorbing more heat from the outside air and starting the process anew.

